Section 10.2.1 Lists
Section 10.2.1 Lists
Section 10.2.1 Overview
The Overview explains Lists and how they are created in WIB Review. You can refer to the Overview to understand lists, their properties, sources and how they are used to automate data extraction.
Section 10.2.1.2 New
Allows you to create a new list from the navigation tree.
Section 10.2.1.2.1 List Types
Section 10.2.1.2.1.1 Comma Separated Value File (CSV)
You can import a CSV file that contains a list of terms with associated values like synonyms, acronyms or values for other attributes in your project. See CSV import process for instructions on importing a CSV List.Section 10.2.1.2.1.2 Website Data Scrape (Roadmap)
You can create a link to a website and schedule data updates from the site. The following use case is a good example of where a website data scrape is recommended:Project Scope: A litigation case where legal discovery involves searching for opioid drugs in the data.Problem: Creating a curated list of prescription drugs and those that are classified as an opioid.Web Scrape Solution: Find a comprehensive public curated list and creating a web scrape.Section 10.2.1.2.1.3 Database Connection (Roadmap)
You can create a database connection to pull data from a database on your intranet. This will require configuration with your Database Administrator.Section 10.2.1.2.1.4 Box Content
You can create a list directly from terms and phrases found in your records. This is ideal if you do not know anything about the records. Each term/phrase is present in the list based on the number of times the term occurs in the records in descending order exposing the terms and phrases that occur most often. Refer Box Content List creation for further instructions.Section 10.2.1.2.1.5 Manual List Creation
Manually create a list like creating an excel spreadsheet list of terms. Name the list, supply a description, and select save. The new empty list is created with the attributes in your workspace. Add Phrases to the list and Hide Phrases that do not add value. Once a phrase is added to the list you can assign other values to the attributes in your list.Section 10.2.1.2.1.6 Import a List from the Library
The library has previously curated industry lists. You can import a list from the library into your project as a starting point. You can edit the list once it is imported into your project. Refer to List Library Import for further instructions.Section 10.2.1.3 Catalog
A grid view of all lists and the properties that define each list.
Section 10.2.1.4 My Lists
Listing of lists in the navigation tree. You can select a list to edit the properties.
Section 10.2.1.5 WIB Library - Lists
Section 10.2.1.5.1 Overview
The Overview explains the List Library. You can search the list library based on the industry. You can choose which industry lists appear in the navigation tree for the WIB Library.
Section 10.2.1.5.2 Catalog
A grid view of all lists in the library and the properties that define each list.
Section 10.2.1.5.3 Save to Library
This feature is only available to Radix Data System Administrators. Please send an email to support@radixdata.com if you would like us to curate a list for your industry/department and add it to the library.
Section 10.2.1.6 Import CSV File
Section 10.2.1.6.1 Create the CSV file
The following details the steps for creating a CSV file for import into WIB™ Review if you chose not to use a curated list from the Library.
Section 10.2.1.6.1.1 Open a spreadsheet
(Excel, Google sheets, Apple Works, etc.)
Section 10.2.1.6.1.2 Label Phrase Column
The phrase column should have the phrase you want the system to find. You do not have to label the column Phrase. You can always associate one column as the phrase column. However, the system will automatically recognize that column when importing the CSV.
Section 10.2.1.6.1.3 Label the added Columns
Label the column(s) based on the information you enter for each column. It is suggested each column matches an attribute field in WIB Review if you want to include the information as an attribute for records. See the example provided.
Save the spreadsheet as a CSV1) From the File Menu in the ribbon select Save As.
2) Give your spreadsheet a name. In the figure below, the spreadsheet is named County Lookup – All States.
3) Using the drop-down menu, select the file type as CSV (Comma-separated values) (*.csv)
4) Navigate to the location you want to save the file by selecting Browse. Remember the location since you will need to import the file into WIB Review from the same location.
5) Select Save.
Section 10.2.1.6.2Select Create List from CSV CardReminder the Create List from CSV card is under Configuration Management, Automation, List, + New List
Section 10.2.1.6.2.1 CSV List Wizard
The wizard will guide you through the process of importing a CSV file.
Section 10.2.1.6.2.2 Input Details
Section 10.2.1.6.2.2.1 List Name
This is the name that will appear in the navigation tree. This name should be short and descriptive.
Section 10.2.1.6.2.2.2 List Description
The description allows you to describe what the list holds and how it will be used for automation. This is only visible on the List View/Edit Page.
Section 10.2.1.6.2.2.3 Upload CSV File
Select the File Upload button. A dialog box will appear click on Select Files… and navigate to the location where you saved the CSV and select the CSV. You can also drag and drop the file onto the dialog. The file will automatically upload once selected or dropped on the dialog.
Section 10.2.1.6.2.3 Import Phrases
Once the CSV is uploaded you must note if the list has headers and which column holds the phrase being looked for.
Section 10.2.1.6.2.3.1 List has Headers
By selecting My data has headers, the system will use the headers as the labels for the columns.
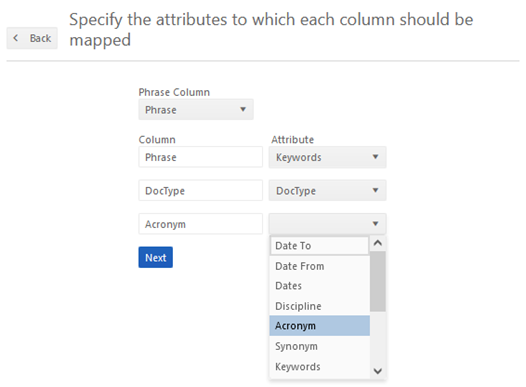
Section 10.2.1.6.2.3.2 Phrase Column
If you have already labeled the column holding the phrase the system will automatically show that column as the phrase column. If it is not labeled as the Phrase column, use the drop down to select which column holds the phrase being looked for.
Section 10.2.1.6.2.4 Link Data to Attributes
You must, at a minimum, link the phrase column to an attribute. If you would prefer an end user to assign the attribute value, we suggest linking the phrase column to the keywords attribute. All phrases from the list that are found will be extracted into the keywords attribute. If your list has other attribute values, you would like populated from the list link those columns to attributes in the system. You can use the drop down to find which attribute is mapped to the data in the CSV.
Section 10.2.1.6.2.5 Review Import
The settings for the new list will be presented for review. You can see which column has the phrase being looked for, the attribute(s) other columns are mapped to, the total phrase count and if any of the data has duplicates. It is important to note that if there are duplicate values the associated field(s) will be combined into a list separated by columns. For example, thirty-one (31) states have Washington County. If you were to link the state from the CSV to an attribute labeled State, the State attribute would display the following list with each value separated by a comma.
STATE: ALABAMA, ARKANSAS, COLORADO, FLORIDA, GEORGIA, IDAHO, ILLINOIS, INDIANA, IOWA, KANSAS, KENTUCKY, LOUISIANA, MAINE, MARYLAND, MINNESOTA, MISSISSIPPI, MISSOURI, NEBRASKA, NEW YORK, NORTH CAROLINA, OHIO, OKLAHOMA, OREGON, PENNSYLVANIA, RHODE ISLAND, TENNESSEE, TEXAS, UTAH, VERMONT, VIRGINIA, WISCONSIN
Section 10.2.1.7 Setup a Web Scrape (Roadmap)
Currently, this feature can only be configured by Radix Data. If you would like to have a web scrape setup, please contact Radix Data at support@radixdata.com.
Section 10.2.1.8 Connect to a Database (Roadmap)
Currently, this feature can only be configured by Radix Data. If you would like to have a database connection setup, please contact Radix Data at support@radixdata.com. You will need to include the database administrator and/or IT in the communication for the setup.
Section 10.2.1.9 Create a List from Box Content
This feature is beneficial if you have no information about the record(s) being processed. This feature is intended for use when you are not completely sure what the records hold. This can be beneficial during the due diligence review phase of a company merger/acquisition, asset acquisitions/divestitures, or when the content is so old the context or inventory does not yield enough information to figure out the content.
Phrases are presented based on the frequency with which they are found in the OCR. N-grams (phrases containing n number of words) are displayed in expanding form building on the initial term to create the desired phrase. The user can filter which OCR text is included in the builder.
Section 10.2.1.9.1 Refining Box Content List Builder Results
You can refine the phrases in the Content Builder through a search or through the filter features listed below
Section 10.2.1.9.1.1 Refine Results via Search
You can reduce the scope of the builder by performing a search if you are interested in specific content. You can continue to run searches until all suspected phrases are found. This is ideal if you know what you are looking for.
Section 10.2.1.9.1.2 Refine Results via Filter Features
If you are starting with a complete unknown, it is suggested using the filter features to break the data into more digestible chunks. You can
Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.1 Collection Filter
Narrow the scope by focusing on a collection of records in the project. This will only work if the record set is broken into collections.Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.2 Session
Narrow the scope to a smaller data set by processing records for a single session.Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.3 Starts With
Process regards according to the first letter or first few letters.
Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.4 First Word Min CharactersThe average word length in the English Dictionary is 4.7 characters. Words with five (5) or more characters, on average, are weighted more than those with fewer characters regardless of how often they occur. Changing the character length returns higher value terms.Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.5 First Word Min Alpha Characters
Terms have numerical values. For instance, H2O is the chemical formula for water. You can also filter out those terms that do not have a minimum number of alpha characters.Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.6 Minimum Frequency
There is no need to review terms that only occur one (1) time in the OCR. Similarly, you may not want to review terms that do not occur less than one hundred (100) times.Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.7 Image Filter
Records are stored in boxes. Most archive boxes have the word box. You may decide that only the images related to the content of a box have the most valuable terms. You can limit the results to the images of content and exclude container images.Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.8 Sort Order
Frequency and count are two different numerical values related to terms. Count stands for the total number of times a term occurs regardless of whether it occurs ten (10) times in a single record. Frequency finds how often the term occurs across the entire population but excludes repetition within a record. In the example supplied the frequency of the term is one (1) and the count is ten (10) if it occurred ten (10) times in only one document.Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.9 Include/Show stop Words
Stop words are inherently excluded from the Phrase builder but you have the choice of showing stop words that may occur in a Phrase. For example, Authority for Expenditure has the stop word for in the middle of the Phrase. The Phrase builder excludes for from the analytics of the phrase. It is included as part of the Phrase when added to the list of terms.Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.10 Show Included/Excluded Words in Results
You can view any words that have been excluded from the results to add them back to the results.
Section 10.2.1.9.1.2.10.1 Filter Results Operators
Operator Usage Guidelines is equal to Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value or multiple values. Results include only records where the data in the column matches the value in the filter. is not equal to Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value or multiple values. Results include only records where the data in the column does not match the value in the filter. is null Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Do not specify a value. The operator tests only for the absence of data in the column. Results include only records where there is no data in the column. is not null Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Do not specify a value. The operator tests only for the presence of data in the column. Results include only records where there is data in the column. contains all Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value or multiple values. Results include only records where the data in the column contains all of the values in the filter. does not contain Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value or multiple values. Results include only records where the data in the column does not contain any of the values in the filter. starts with Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value. Results include only records where the data in the column begins with the value in the filter. ends with Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Specify a single value. Results include only records where the data in the column ends with the value in the filter. is empty Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. An empty string is used to point to a unique string with zero length where NULL is used to refer to nothing. Results include only records where string with zero length. is not empty Valid for a column that contains text, numbers, or dates. Do not specify a value. The operator tests only for the presence of data in the column. Results include only records where there is data in the column. Section 10.2.1.9.2 List Grids
There are three grids on the List Builder: Phrases, Search Results, and Related Phrases. A description of each along with how they are used to build a list are described below.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.1 Phrase List
As you add terms to the list, they appear in the Phrases List. These are the terms the system will find automatically when the phrase is found in the OCR. You can have these phrases populate an attribute or you can have the phrases populate a keyword field. Keywords can be helpful when searching for records but are not needed as part of the record index.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.2 Search Results List
These are the phrases that match the criteria of the search parameters. As you refine the search criteria the phrases are filtered. The search results are listed in order by the first term, the beginning word, and then expanded upon with each successive word. Phrases are capped at 5 words. You can choose whether to show words that you have excluded from the search results and/or those words that have already been added to the list.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.2.1 Show/Hide Included Words
To see only those phrases that you have not included in your list turn off the Included Words.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.2.2 Show/Hide Excluded Words
To see only those words that you have not excluded from the list turn off the show excluded words.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.3 Related Phrases
Related phrases are those that have the selected term from either the phrase list or the search results. Related phrases list all the other phrases having the selected term and/or phrase. This can help expose terms you might want to find but did not know where in the records being processed.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.3 Including Phrases
Once you find a phrase you want the system to find for each record having the phrase, use the select box in the Search Results or Related terms to check it and then select include from the list where the term was selected.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.4 Excluding Phrases
You may find phrases that occur often in the OCR but are of no importance and become noisy when reviewing term clusters. You can prevent these from appearing in the analysis by selecting the Phrase from the Search Results and Excluding the phrase. You can always add a Phrase back to the list if it is later figured out to have value.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.5 Associating Synonyms
WIB supports stemming however, you may want to manually include terms that are similar in structure and the same in meaning. For example, Authority for Expenditure means the same thing as Authorization for Expenditure. The stemming will find the two different values, but you can also add the synonym to the term. You can select a term from the list and a term from the Related phrases and then select synonym and the related phrase will be added as a synonym to the phrase in the list.
Section 10.2.1.9.2.6 Associating Acronyms
Phrases are commonly referred to by the Acronym of the term. Taking the example from the synonyms Authorization for Expenditure is commonly referred to as AFE. You can also associate the acronym for a term when adding it to a list.
 Section 10.2.1.10 Manually Create a List in WIB Review
Section 10.2.1.10 Manually Create a List in WIB Review
You can create a list manually directly into WIB Review
without viewing the results from the OCR or creating a separate Comma-separated Values (CSV) File. The
process is like creating a CSV.
Section 10.2.1.10.1 Input Details
Name the list and a description.
Section 10.2.1.10.2 Show Columns needed for list
Use the column selector to show those needed for the list and to hide those that are not needed.
Section 10.2.1.10.3 Add a Phrase
Select Add a Phrase for each value you want to add to the list.
Section 10.2.1.10.4 Manually Enter Phrases
Enter the phrase and associated metadata. Notice the same attributes in the grid are present in the input dialog.
Section 10.2.1.10.5 Add Phrases from Box Data
Refer to Create a List from Box Content for instructions on adding phrases from box data to a manually created list.
 Section 10.2.1.11 Import a List from the Library
Section 10.2.1.11 Import a List from the Library
Related Articles
Section 10.2.4 Taxonomy
Section 10.2.4 Taxonomy A Taxonomy in WIB is the combination of lists and regular expressions and how they are used to classify records. Section 10.2.4.1 Overview Explains what a taxonomy is and how it is used in WIB Review. Section 10.2.4.2 New ...Section 1 Getting Started
Previous Article: Getting Started The Review Platform for What’s in the Box is designed to provide end users access to the photographs of records with the extracted data configured in the Platform. This allows for users to use the analytics, auto ...Section 10.2 Automation
Section 10.2 Automation Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes. Human intervention is reduced by predetermining decision criteria, sub-process relationships, and related actions — and embodying ...Section 1.3 Portal
Previous Article: 1.2 Login Section 1.3 Portal The portal supplies quick access to your workspace(s) and resources having key information. Section 1.3.1 Workspace A workspace is a secure private online space. Workspaces function on an invite only ...Section 13.6 Export History
Section 13.6 Export History The export history lists the images for all the exports. The following system attributes are listed for each image; Box Identifier, Image Filename, Export Package, Configuration, Username, Exported Text (Boolean), Exported ...